Breaking barriers in smart metering with Wi-Fi HaLow: Smart meters are revolutionizing energy management, but traditional communication methods often fall short. Wi-Fi HaLow, with its long range, low power consumption, and robust security features, offers a compelling solution to overcome these limitations. This guide explores how Wi-Fi HaLow is transforming the landscape of smart metering, addressing key challenges and unlocking new possibilities for efficient energy grids.
We’ll delve into the technical specifications of Wi-Fi HaLow, comparing it to other technologies like Zigbee and cellular networks. We’ll then dissect the practical aspects of network design, deployment, and data management, offering insights into overcoming security concerns and regulatory hurdles. Finally, we’ll examine real-world case studies and explore the exciting future potential of Wi-Fi HaLow in the ever-evolving world of smart energy.
Wi-Fi HaLow in Smart Metering: A Deep Dive
Smart metering is revolutionizing the energy sector, enabling real-time monitoring and control of energy consumption. However, effective communication between smart meters and the central grid remains a crucial challenge. Wi-Fi HaLow, a low-power, long-range variant of Wi-Fi, emerges as a promising solution, addressing many limitations of traditional communication protocols. This article explores the capabilities of Wi-Fi HaLow in smart metering, examining its advantages, challenges, and future potential.
Wi-Fi HaLow Technology and its Advantages
Wi-Fi HaLow operates in the 900 MHz frequency band, offering several key advantages over other technologies. Its long range, low power consumption, and ability to penetrate obstacles make it ideal for wide-area smart metering deployments. Unlike Zigbee or other short-range protocols, Wi-Fi HaLow eliminates the need for dense network deployments, reducing infrastructure costs. Traditional smart metering infrastructure often struggles with limited range, high power consumption, and susceptibility to interference.
Wi-Fi HaLow directly addresses these issues, enabling cost-effective and reliable data transmission even in challenging environments.
Comparative Analysis of Communication Protocols
A comparison of Wi-Fi HaLow, Zigbee, and cellular technologies highlights Wi-Fi HaLow’s strengths in specific contexts. The table below summarizes key differences:
| Technology | Range | Power Consumption | Cost | Data Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wi-Fi HaLow | 1 km+ | Low | Medium | Medium |
| Zigbee | 10-100m | Very Low | Low | Low |
| Cellular (e.g., LTE-M, NB-IoT) | Wide Area | Medium-High | High | Medium-High |
Overcoming Barriers to Wi-Fi HaLow Adoption
Despite its advantages, Wi-Fi HaLow faces hurdles to widespread adoption. Interoperability concerns, where different devices may not communicate effectively, and security vulnerabilities are significant challenges. Addressing these requires careful planning and implementation.
Mitigating Security Risks
Robust security measures are crucial for Wi-Fi HaLow smart metering networks. Strong encryption, such as AES-128 or AES-256, protects data in transit. Authentication protocols, like WPA3, prevent unauthorized access. Regular firmware updates are essential to patch security vulnerabilities and maintain a secure network.
Regulatory Hurdles and Standardization
Regulatory compliance and standardization are essential for successful Wi-Fi HaLow deployments. Different regions have varying regulations regarding spectrum allocation and device certification. Standardization efforts ensure interoperability and promote wider adoption. Active participation in relevant standards bodies is vital for navigating these challenges.
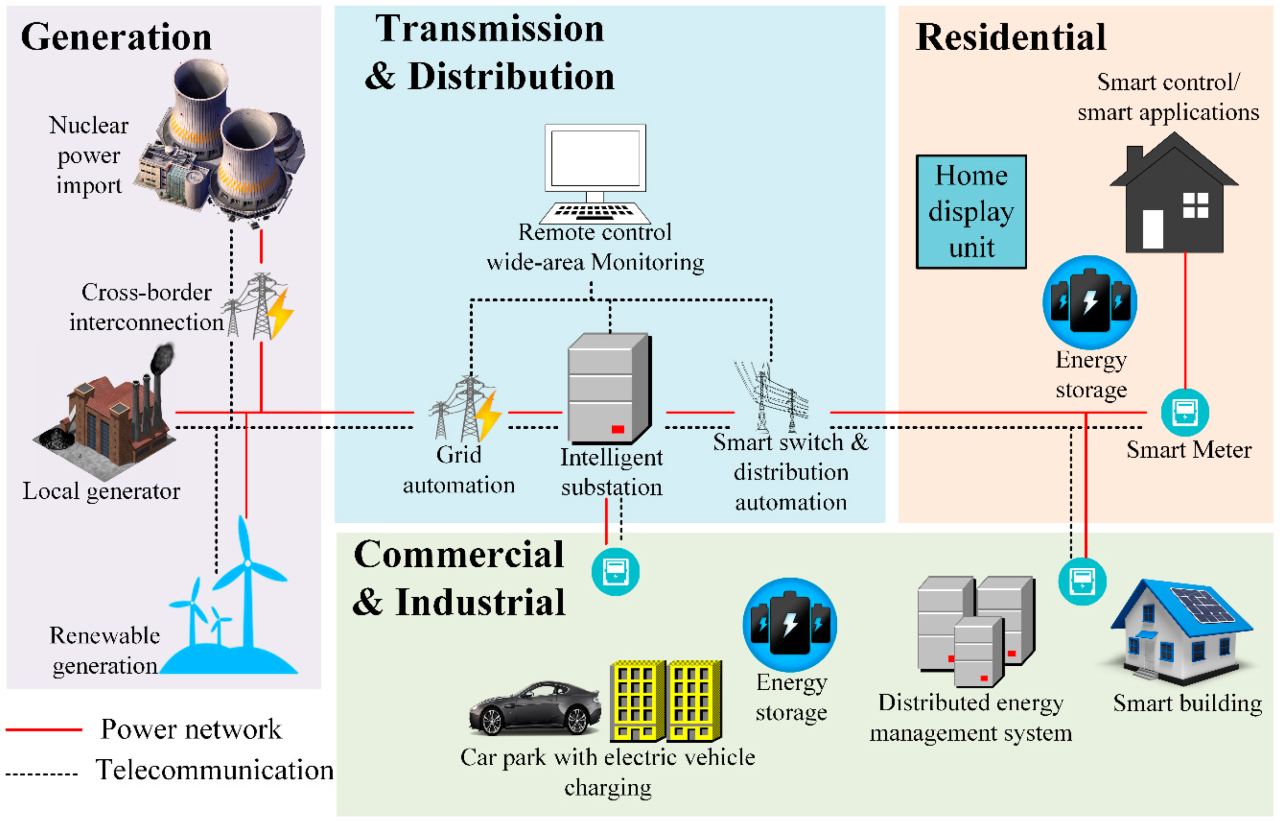
Wi-Fi HaLow Network Architecture for Suburban Deployment
A sample Wi-Fi HaLow network for a suburban area might employ a star topology. Smart meters (nodes) would connect to a central gateway located at a strategically chosen point, perhaps a substation or a central hub within the area. Node placement would consider factors such as building density and terrain, aiming for optimal coverage and minimal signal interference.
The gateway would then connect to the utility’s central data management system. This design allows for efficient data collection and management across a relatively large geographical area.
Smart metering is getting a serious upgrade thanks to Wi-Fi HaLow’s long-range, low-power capabilities. Want to learn how it’s revolutionizing data collection and reducing infrastructure costs? Check out this informative article on Breaking barriers in smart metering with Wi-Fi HaLow to see how Wi-Fi HaLow is overcoming challenges in remote areas and dense urban environments. This technology is making smart grids more efficient and reliable than ever before.
Impact of Environmental Factors
Environmental factors significantly impact Wi-Fi HaLow network performance. Obstacles like buildings and trees can attenuate signals, reducing range and reliability. Interference from other devices operating in the 900 MHz band can also degrade performance. Careful site surveys and network planning are crucial to mitigate these effects. Using directional antennas can improve signal strength and reduce interference.
Configuring and Managing a Wi-Fi HaLow Network
Effective network management is essential for maintaining optimal performance and security. The following steps are key:
- Device Provisioning: Assigning unique identifiers and security credentials to each smart meter.
- Network Configuration: Setting up the gateway, including SSID, security settings, and network parameters.
- Firmware Updates: Regularly updating the firmware on both smart meters and the gateway to address bugs and security vulnerabilities.
- Monitoring and Maintenance: Continuously monitoring network performance and addressing any issues promptly.
Data Management and Analytics with Wi-Fi HaLow
Efficient data management is crucial given the large volumes of data generated by smart meters. Techniques like data compression and aggregation can reduce transmission overhead. Secure data transmission protocols ensure data integrity and confidentiality.
Ensuring Data Integrity and Security
Data integrity and security are paramount. Using encryption during transmission and employing secure storage solutions protect against unauthorized access and data corruption. Regular audits and security assessments help maintain a robust security posture.
Leveraging Data Analytics for Improved Grid Management
Data analytics transforms raw meter data into actionable insights. For instance, identifying peak demand periods allows for optimized grid management and load balancing. Predictive maintenance based on meter data reduces outages and improves system reliability. Anomaly detection can flag potential issues, such as theft or equipment malfunction. These analytics improve energy efficiency and grid reliability.
Case Studies and Future Trends, Breaking barriers in smart metering with Wi-Fi HaLow
Several successful Wi-Fi HaLow deployments in smart metering demonstrate its effectiveness. While specific details of projects are often proprietary, examples exist in various regions showing the technology’s capability to handle large-scale deployments in diverse environments. Challenges encountered often relate to integrating with existing infrastructure and ensuring robust security.
Okay, so we’re talking about how Wi-Fi HaLow is changing the game for smart meters, right? It’s all about long-range, low-power communication. Completely unrelated, but sadly, I just saw the news that Atlanta rapper OG Maco dies at 32, family confirms , which is a real bummer. Anyway, back to smart meters – HaLow’s making widespread deployment much more feasible and cost-effective.
Future Potential of Wi-Fi HaLow
Wi-Fi HaLow’s future looks bright. Advancements in low-power technologies will further enhance its efficiency. Integration with IoT platforms enables broader applications beyond smart metering, creating a more interconnected energy ecosystem. Continued standardization efforts will improve interoperability and drive wider adoption.
Wi-Fi HaLow in Different Geographical Locations
The success of Wi-Fi HaLow deployments varies across geographical locations due to differing regulatory environments and environmental factors. Dense urban areas may experience higher levels of interference, requiring careful network planning. Rural areas, with their longer distances between meters, benefit from the technology’s extended range. Regulatory compliance, spectrum availability, and the cost of infrastructure all play a role in determining the feasibility and success of Wi-Fi HaLow deployments in different regions.
Conclusion: Breaking Barriers In Smart Metering With Wi-Fi HaLow
Wi-Fi HaLow presents a powerful solution for overcoming the challenges inherent in smart metering deployments. Its unique combination of extended range, low power consumption, and enhanced security makes it an ideal technology for building robust and efficient energy grids. By addressing technical barriers and navigating regulatory landscapes, the widespread adoption of Wi-Fi HaLow promises a future of improved energy management, reduced costs, and enhanced grid stability.
The potential for data-driven insights and integration with other IoT platforms further solidifies its position as a key player in the smart energy revolution.
Answers to Common Questions
What is the typical range of a Wi-Fi HaLow network in a smart metering context?
The range varies depending on factors like terrain and interference, but it generally extends much further than other short-range technologies like Zigbee, often reaching several kilometers.
How does Wi-Fi HaLow ensure data security?
Smart metering’s getting a huge boost with Wi-Fi HaLow, tackling range and power issues that held it back. Think about the possibilities – it’s like learning about a cool new tech, then discovering a completely unrelated story, like this article about a hockey player’s fan in Florida: Dobes aura une admiratrice particulière en Floride – TVA Sports.
Anyway, back to Wi-Fi HaLow; its low-power, long-range capabilities are changing the game for widespread smart meter deployment.
Wi-Fi HaLow utilizes robust encryption methods and authentication protocols to protect data transmitted between smart meters and the network gateway. This minimizes the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
What are the costs associated with implementing Wi-Fi HaLow in a smart metering system?
Costs vary depending on the scale of deployment and the specific hardware and software chosen. However, the long-term benefits in terms of reduced energy consumption and improved efficiency can often outweigh the initial investment.
Is Wi-Fi HaLow compatible with existing smart meter infrastructure?
Compatibility depends on the specific smart meter models and existing network infrastructure. Retrofitting may be required in some cases, but the overall integration process is often smoother compared to other technologies.